- This event has passed.
World Biodiversity Day
May 22, 2019 @ 08:00 - 17:00

 The UN bases this year’s event on sustainable development. Do you know to what extent we depend on biodiversity?
The UN bases this year’s event on sustainable development. Do you know to what extent we depend on biodiversity?
“Humanity’s fate is tightly linked with biological diversity – the variety of life on earth. Biodiversity is essential for sustainable development and human well-being. It is crucial to the reduction of poverty, due to the basic goods and ecosystem services it provides.”
This is the message used by the United Nations (UN) to present the Biological Diversity Day, whose theme this year focuses on Biodiversity for sustainable development. This global event, which is held on the 22nd of May since year 2000 –it was created in 1993 but its first seven editions were held on the 29th of December-, aims to promote and raise global awareness of issues related to the planet’s biodiversity. And it is not a coincidence that the thesis this year deals with sustainability, it is a complementary action along with the Sustainable Development Goals, which will be introduced in New York in four months.
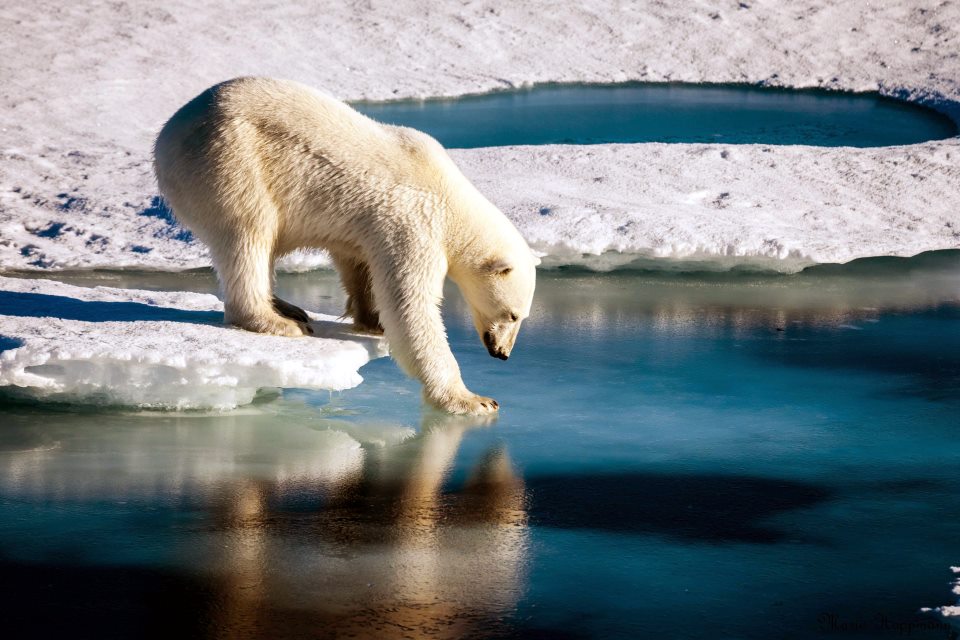
Global warming threatens the polar bear
Did you know that more than 3 billion people depend on marine and coastal biodiversity, while over 1.6 billion people rely on forests and non-timber forest products for their livelihoods?
Just as the latest IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) report says, climate change could have a negative and irreversible impact if human action is not modified. The future of biodiversity is highly threatened by climate change, but we can still do something.
There are several species that have already suffered irreversible consequences or are just about to do it:
- Three species disappear every hourCloud forests are running out of frogs
- From 100 to 150 species disappear every day
- From 15.000 to 80.000 species disappear every year

These figures, despite their large size, are no more than figures. But if we picture them on a familiar face, they can make us more aware of what we are losing:
- The polar bear population in Canada has decreased by 22% in the last thirty years as a result of climate change. The melting of the poles causes a decrease in food for hunting and an increase of the distances sometimes impossible to swim. Their malnutrition prevents them from spending the winter with guarantees of survival.
- Up to 74 species of cloud forest frogs have already disappeared due to the environmental dryness caused by global warming. These amphibians need specific humidity conditions for incubating their eggs and this conditions are no longer happening in many ecosystems.
- The Adelie penguin population in Antarctica decreased over the last twenty years from 320 pairs to 54 pairs. Why? The increase of 5,5 0C in that area over the last half century has forced the massive exodus of the krill, a kind of crustacean that represents their main food source, towards colder waters these penguins cannot easily reach.
- The flycatcher, a species of bird that lives in the Netherlands, has experienced a 90% population decrease in a few decades. Once again, the Pingüinoscause is a change of behaviour amongst his food supply caused by climate change. The young birds in this species are usually born when caterpillars hatch. With the gradual temperature raise, caterpillars began to anticipate their hatching a fortnight, so when flycatcher babies are born, their parents can’t find caterpillars to feed them.
These sad examples are just a small sample of how humans mistreat biodiversity. The IPCC says that 50% of all reported species have been negatively affected in recent years by climate change.
- Read more here.


